Medications For Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding The Diabetes Treatment
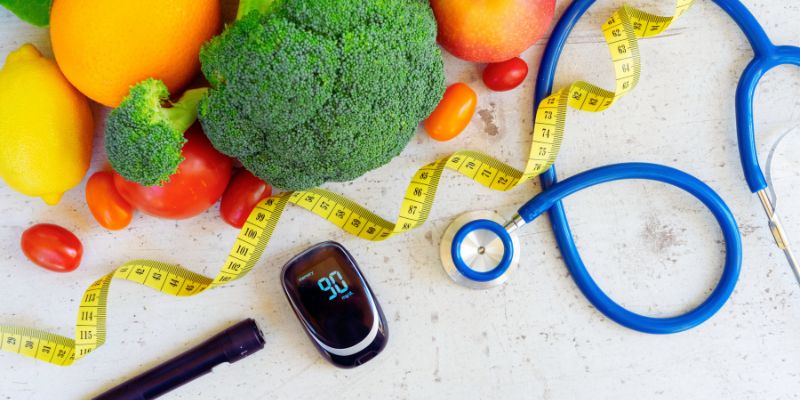
Diabetes causes higher blood sugar levels because the body cannot make or use insulin. Lifestyle choices, including healthy eating habits, exercise, and weight management, can help manage conditions like type 2 diabetes. However, most people also need different medicines to keep their blood sugar levels normal and prevent related health problems.
Some of these medicines are taken orally, while others are injected. Patients must take these medicines for the rest of their lives, but the dose can vary with time. If you are still interested in learning more about type 2 diabetes medications and how they work, keep reading and

Oral Medicines For Type 2 Diabetes
Several medicines, including Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants (BASs), DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins), and Sulfonylureas, are used worldwide to manage diabetes. Let's understand here how these medicines help you prevent and manage type 2 diabetes:
- Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: These medicines slow down the breakdown of foods containing starch, such as potatoes, pasta, rice, etc. They also inhibit the absorption of larger carbohydrate molecules in the small intestine. Plus, these medicines convert larger molecules that are difficult to absorb into ones the body can easily absorb. They also lower blood sugar by 0.5%0.8% over several months. Many diabetics take a pill with the first bite of their meal, and most patients take up to three pills daily.
- Bile Acid Sequestrants (BASs): These medicines help greatly lower your cholesterol level. The molecules in this medicine block bile acid in your stomach, so your blood cannot absorb it. The less absorption of bile acid by blood will give a signal to your liver. It will start taking cholesterol from your blood and produce bile acid. Thus, this mechanism helps manage blood cholesterol levels. Lower cholesterol levels in the blood help lower blood glucose levels and maintain blood sugar.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors (Gliptins): These medicines work by increasing the secretion of incretin, a type of hormone. It includes GLP1, which results in the secretion of GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). It inhibits the production of glucagon and stimulates the production of insulin. Glucagon is a hormone the pancreas produces to release glucose molecules in your bloodstream. It is released by alpha cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that is secreted by beta cells in the pancreas. Through this mechanism, DPP-4 inhibitors directly lower blood glucose levels.
- Sulphonylureas: These medicines directly affect insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas and help suppress glucagon secretion. This mechanism discontinues if a person stops taking sulphonylureas. They increase the direct production of insulin from the pancreas and help enhance insulin action in your body.
- Thiazolidinediones: They contain glucose transporter proteins. These medicines help by increasing the brain's demand for energy. Insulin production cells are activated to release energy, and the liver decreases glucose production and secretion. Hence, insulin resistance is reduced.
Injectable Medications For Type 2 Diabetes
Several types of injections are also available, which many people with type 2 diabetes use to maintain their blood sugar levels. Dulaglutide (triplicity), Semaglutide (Ozempic), and Liraglutide are the most commonly used injections. Let's learn about these injections in detail here:
- Dulaglutide: This injection is taken once a week. It works by activating beta cells in the pancreas to increase production and suppressing alpha cells to inhibit glucagon production. By doing so, blood sugar remains at a normal level. This injection is very helpful for maintaining postprandial glucose levels. It does this by delaying gastric emptiness. This process also slows down as time passes until the next dose is injected.
- Semaglutide: This injection is also taken once a week. It binds to GLP-1 receptors, activating insulin production and inhibiting glucagon secretion. It greatly helps in weight management. It is best for people with diabetes and obese people. A calorie-deficit diet and a more active lifestyle are always recommended for weight management.
- Liraglutide: Liraglutide has been shown to work well in lowering fasting and postprandial glucose levels. It also helps maintain weight, especially for diabetics, by delaying gastric emptiness. It also reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases in people with type 2 diabetes.
Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes With Diet And Lifestyle
A healthy diet and keeping yourself active can help you maintain blood sugar levels and diabetes management. Lets understand here in detail how food and active lifestyle can help to do that:
- Food And Diabetics: Diabetics should eat a variety of food (fruits and vegetables) and avoid food items containing sugar, carbohydrates, and fats. Thats because these foods are directly linked to increased blood glucose. Weight management is also important for people with diabetes. A healthy and balanced diet will help you achieve this goal. Also, it can greatly help you manage your blood sugar level. You can reduce calories by taking smaller serving sizes and more fibrous foods. Plus, ask a nutritionist to make you a diet plan that works best for your current body type. Aside from that, never miss a meal, especially if you are taking medicines; it can cause hypos.
- Active Lifestyle And Diabetics: Physical exercises can help manage diabetes. For example, muscle-intensive exercises with a little walk help utilize carbs from the muscles and eventually from the blood, lowering blood sugar levels. Therefore, you should aim for 2.5 hours of activity each week to lower the risk or management of diabetes type 2. Also, it will help you to maintain a healthy body weight. Remember that lower body weight can help lower your blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. Eventually, it can also lower the risk of various other health problems.
Conclusion:
There are several medications to manage diabetes, including oral and injectable. All of these medicines have different mechanisms of action. For example, some boost insulin production, and others reduce blood sugar levels. Also, remember that not all medicines work on every diabetic patient. To know which medicines suit you well, always consult your doctor. Besides that, healthy diets and lifestyles also help manage diabetes to a greater extent. When you do exercise, muscles utilize glucose stored in the form of carbs. It automatically lowers blood glucose levels as carbs eventually break down in glucose. Understanding how all these mechanisms help lower blood sugar, any individual can help himself get a healthier and better life!