Why Play-Based Learning Matters in Early Childhood Education
Playing is both fun and important for learning when you are a child. Play's importance in a child's development has been understood for many years, and it is still a key component of early childhood education. Play-based learning, which uses planned games to teach important skills, is being used increasingly by schools and teachers worldwide.
This way of teaching kids isn't just fun and helps them improve their physical, mental, social, and emotional skills. Young children learn about the world, try new ideas, and make sense of their experiences through play. In this blog post, we will discuss the many benefits of play-based learning and why it is such an important part of early childhood education.
What is Play-Based Learning?
Play-based learning is a way of teaching that lets kids explore, make things, and learn while they play. This method is lively and engaging so that kids can connect with the information in a fun and useful way. Play-based learning gives kids more control over their learning than standard, teacher-led education focusing on organized lessons.
Kids in play-based classes do things like pretend play, building with blocks, arts and crafts, and group games. Instead of giving straight instructions, the teacher's job is to watch, guide, and offer chances for discovery. Through these exercises, young people learn things and develop skills that will help them in school.
The Cognitive Benefits of Play-Based Learning
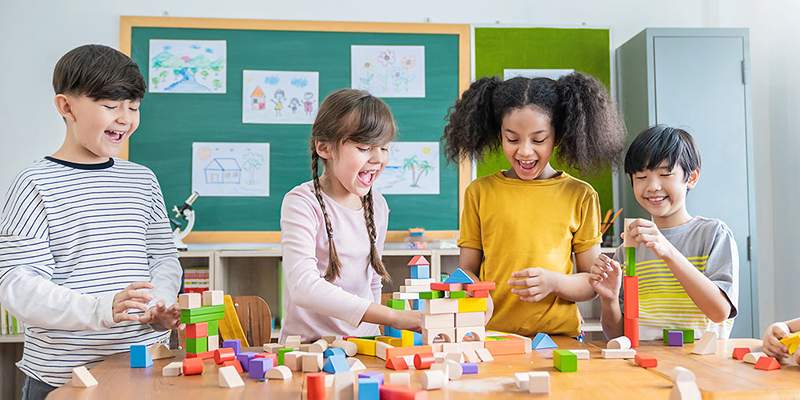

One of the best things about learning through play is that it helps children's brains grow. Cognitive development is how kids think, learn, and understand the world. Kids learn to think critically, solve problems, and be creative through play.
1. Enhances Problem-Solving Skills
When kids learn through play, they often face hurdles that make them think critically and figure out how to fix problems. They know how to look at problems from different points of view as they build a tower out of blocks or figure out how to put together materials for a project. These activities help kids learn to think logically and keep going even when things get hard. These are important skills for future learning.
2. Stimulates Creativity and Imagination
Creative play is one of the most enjoyable aspects of play-based learning. Activities such as pretending to be different characters, building imaginative worlds, or creating art allow children to stretch their imaginations. This fosters creativity, a key component of cognitive development and a valuable skill in all areas of life.
3. Promotes Language Development
In play-based environments, children often engage in conversation with peers and adults. Role-playing activities, such as pretending to cook in a pretend kitchen or acting out a story, encourage children to practice new vocabulary, sentence structures, and communication skills. These social interactions help children improve their language skills, which are critical for academic and social success.
The Social and Emotional Benefits of Play-Based Learning
Aside from cognitive development, play-based learning also profoundly impacts a child's social and emotional growth. Children learn how to interact with others, manage their emotions, and build relationships through play. The social dynamics that play-based activities foster are essential for developing interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence.
1. Fosters Cooperation and Teamwork
Many play-based activities involve working with other children to achieve a common goal. Whether building a fort, playing a team sport, or organizing a group game, children learn how to collaborate with others. These experiences teach children about cooperation, sharing, and empathy, which are important life skills.
2. Helps Develop Emotional Regulation
Play allows children to express their emotions in a safe and supportive environment. Through role-play or engaging in scenarios that evoke different feelings, children can process their emotions, understand their feelings, and learn how to manage them. This emotional regulation is key to developing self-control, resilience, and a positive self-concept.
3. Builds Confidence and Independence
Children who are free to explore and make decisions during play gain confidence in their abilities. They develop a sense of autonomy as they learn to take initiative and navigate challenges independently. These experiences help children feel more confident in their abilities, leading to a positive self-image and greater success in school and life.
The Physical Benefits of Play-Based Learning
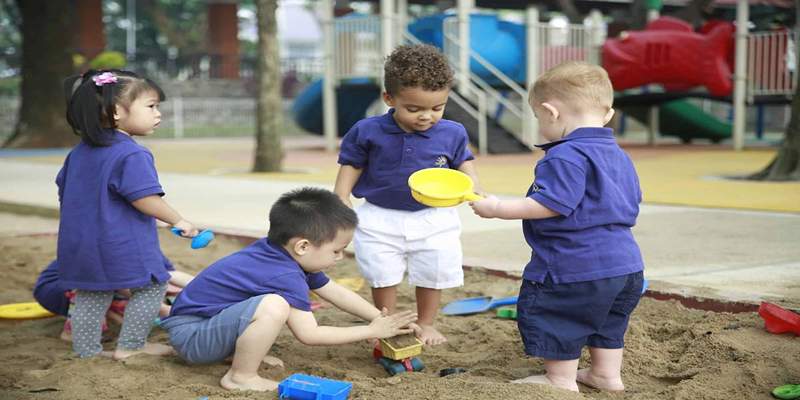

Physical development is another important aspect of early childhood education. Play-based learning encourages physical activity, which is crucial for young children's growth and development. Children develop strength, coordination, and motor skills through movement and active play.
1. Enhances Fine and Gross Motor Skills
From running and jumping to drawing and building with small blocks, play activities help children develop fine and gross motor skills. Fine motor skills are necessary for tasks like writing, using scissors, or manipulating small objects, while gross motor skills are needed for walking, running, and climbing. Play provides opportunities for children to practice and refine these motor skills, essential for daily life and academic success.
2. Encourages Physical Activity
In today's digital age, it's easy for children to become sedentary, but play-based learning encourages them to be active. Outdoor play, such as running, climbing, or playing ball games, helps children develop physical strength, stamina, and coordination. Active play also contributes to healthy physical development, helping to reduce the risk of childhood obesity and promoting overall well-being.
The Role of Educators in Play-Based Learning
In play-based learning, the role of the educator is pivotal. Rather than being the sole instructor, teachers become facilitators of learning. They create environments that encourage curiosity, exploration, and social interaction. Educators guide children through play, offering new challenges, asking thought-provoking questions, and introducing new materials.
Teachers also observe and assess children's progress through play, which provides valuable insights into each child's development. This allows educators to tailor their support to meet each child's individual needs, fostering a more personalized and effective learning experience.
Conclusion
Play-based learning is not just an enjoyable way for children to pass the time; it is an essential part of their development. It nurtures cognitive, social, emotional, and physical skills to serve children throughout their education and beyond. By allowing children to learn through play, educators provide the tools they need to succeed in school and life.
As we continue to understand the value of play in early childhood education, it is crucial to embrace this approach and prioritize play as a central element of the learning experience. In doing so, we can ensure that children are not only ready for academic challenges but also well-equipped for the complex world they will encounter.