Blood Glucose Test: Everything You Need To Know About Diabetes Screening Test
Usually, people experience low or high blood sugar levels based on their diet, lifestyle, and other health issues. Well, what does each level mean? How much blood sugar is considered normal, pre-diabetic, or diabetic? How is diabetes diagnosed? If, like many other people, you have the same queries in mind, you have reached the right place.
By understanding how blood sugar levels behave during certain parts of the day, before and after meals, you can better analyze your health. Plus, it will help you make the required changes in diet and lifestyle, which can prevent complications beforehand. Blood glucose or sugar tests can help you monitor and maintain blood glucose levels. They can also serve as a great help in understanding energy levels, appetite, and other related aspects. So, let's get into the details without further delay and learn more about these tests!
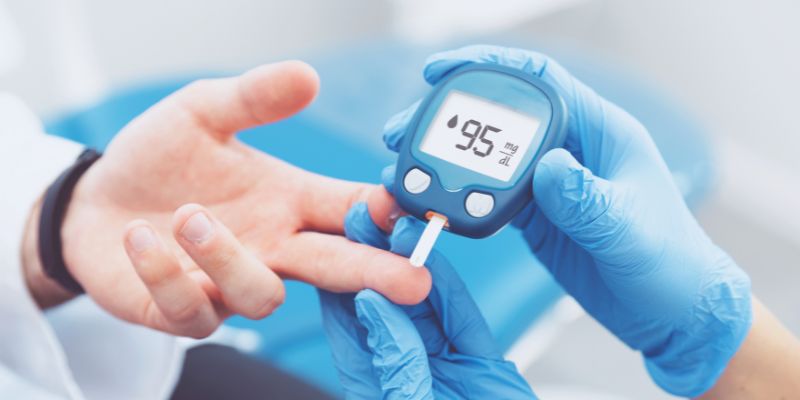
Understanding Blood Glucose And Diabetes
Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the amount or level of sugar in your bloodstream. It comes from the foods we eat, especially carbohydrates and sugary items, which are then broken down into glucose, the main energy source in our body. Remember that glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day. The variations can differ for a healthy and diabetic person based on diet, lifestyle, and overall health.
Maintaining and monitoring blood glucose levels is very important for overall health as it affects many organs, causing damage that is not controlled on a timely basis. Also, excessive glucose can cause insulin resistance and can lead to diabetes. There are two different types of diabetes, including the following:
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D): In T2D, glucose from food, mainly carbohydrates, and sugar, is not properly absorbed into the bloodstream and taken up by the muscles. It happens because of insulin resistance or decreased insulin production from the pancreas, which is responsible for the effective breakdown of glucose. This type of diabetes is seen in people ages 18 and up. It is reversible to a greater extent if dealt with care.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks and kills the pancreas (especially insulin-producing beta cells). This type of diabetes is common in children and young adults, so it is also known as juvenile diabetes. Remember that type 1 diabetes needs lifelong insulin therapy.
When Do You Need To Check The Blood Sugar Levels?
Some symptoms may indicate fluctuating blood sugar levels. For example, you may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and sores. It happens because of high blood glucose levels. You can witness shakiness, sweating, hunger, dizziness, anxiousness, and confusion, if not that. All of these indicate the low glucose levels.
Remember that regular testing helps you monitor glucose levels and make necessary lifestyle changes to maintain health. Understanding these levels is vital for effective management, especially for those with diabetes. Now, you might be thinking about how you can test the blood glucose level. Well, there are two common types of blood glucose tests:
- Capillary Blood Glucose Test: The test is usually done through a finger prick. A test strip and a glucose meter are used, and the results are shown immediately.
- Plasma Blood Sugar Test: The blood is drawn from veins and sent to the laboratory to test and analyze sugar levels.
Plasma blood glucose tests provide more accurate results than capillary tests. However, to keep blood sugar levels in check, one can opt for a glucometer for an instant result at home.
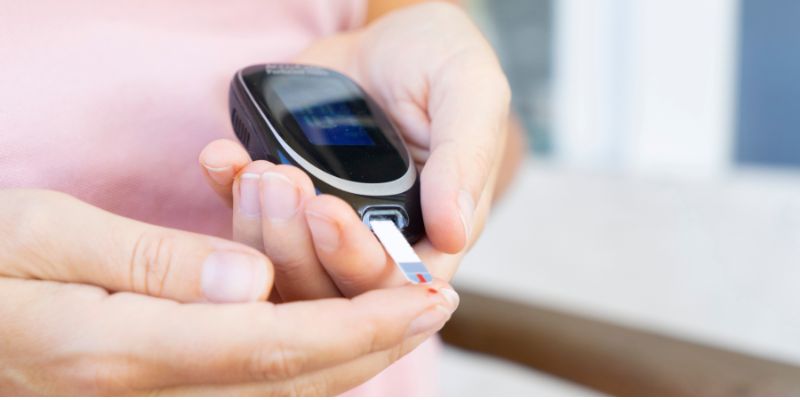

Blood Sugar Test: Diagnosis Of Type 1, Type 2, And Pre-Diabetes
Now, lets know about different blood sugar tests in detail here and see what different glucose level says:
A1C Test:
It is also known as the HbA1c or glycated hemoglobin test. The glycated hemoglobin test measures how much hemoglobin (blood protein) is covered with glucose molecules. It shows how well oxygen from your blood is transported. The test assesses variations in blood sugar levels for a longer term, about 2-3 months, rather than a daily checkup. Remember that higher A1C levels show the risk of diabetes-related complications. Here are the key A1C ranges:
- Normal: If it's below 5.7%
- Pre-Diabetes: If it ranges from 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: If it is 6.5% or higher
Fasting Blood Sugar Test:
The test measures how much blood sugar one has if they do not have their meal in at least 6-8 hours. It helps to understand how well sugar is being utilized in the form of energy. The high insulin resistance would prohibit energy consumption from glucose in the blood, resulting in underutilized sugars. It will result in higher sugar levels in the blood. The key ranges are as follows:
- Normal: If it is 70 to 99 mg/dL
- Pre-Diabetes: If it is 100 to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: If it is 126 mg/dL or higher
Random Blood Sugar Test:
A random blood sugar test can be done at any time throughout the day, regardless of when you had your last meal and what you had in your meal. It does not vary significantly for healthy people, but it is not a good sign if they do. Here is what your test results indicate:
- Normal: The normal blood sugar level will always be less than 200 mg/dL
- Diabetes: If your sugar level is 200 mg/dL or higher, you have diabetes. This condition can also cause other symptoms, such as frequent urination, increased thirst, or fatigue.
Glucose Tolerance Test:
The glucose tolerance test is performed to asses at what speed does your body breakdown glucose from your food, mainly from carbohydrates and sugary items. It also tells you how quickly glucose is absorbed into your bloodstream and muscles. Here is what the results interpret:
- Normal: If it is less than 100 mg/dL with fasting and less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after having meals
- Pre-Diabetes: If it is 100 to 125 mg/dL with fasting and 140 to 199 mg/dL 2 hours after meal
- Diabetes: If it is 126 mg/dL or higher with fasting 200 mg/dL or higher 2 hours after a meal
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test:
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a procedure used to assess how well your body processes glucose and gestational diabetes. Results interpretation:
- Normal: If it is less than 100 mg/dL with fasting and less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after having the meals
- Pre-Diabetes: If it is 100 to 125 mg/dL with fasting and 140 to 199 mg/dL 2 hours after having the meal
- Diabetes: If it is 126 mg/dL or higher with fasting and 200 mg/dL or higher 2 hours after having the meal
Conclusion:
Whether you think you are diabetic or about to become one, perform the blood sugar test to monitor your blood sugar levels and solve this mystery. For that, you can visit the laboratory or bring home a kit (glucometer) to test blood sugar levels on your own. If your blood glucose level is above 200mg/dl, you must control your diet and strictly change your lifestyle. But, if it is below 100mg/dl even after you just had food, there is also a problem. Therefore, you must consult your doctor. Always check your blood sugar levels and take healthy steps to prevent high or low ones!